Automation Solutions
Take the Next Step
Start Making an Impact Today
Free Consultation? 9654699125
Track Trace Solution
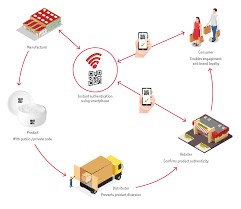
A track and trace solution is a system or technology used to monitor and trace products, goods, or assets throughout their entire supply chain journey. It enables companies to have real-time visibility and control over their products’ movement, from the manufacturing or production stage to distribution and retail. The primary goal of a track and trace solution is to ensure product authenticity, enhance supply chain transparency, and combat counterfeiting, diversion, and theft.
Key components and features of a track and trace solution typically include:
- Serialization: Each individual product or packaging is assigned a unique identifier, often in the form of a barcode, QR code, RFID tag, or alphanumeric code. This serial number allows each item to be uniquely identified and tracked throughout the supply chain.
- Data Capture and Recording: Track and trace solutions collect and record data at various points in the supply chain. This data may include information about production dates, batch numbers, manufacturing locations, distribution centers, and shipping details.
- Integration with Manufacturing and ERP Systems: The track and trace system is often integrated with the company’s manufacturing and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This integration ensures seamless data flow and enables real-time updates on inventory levels and product movement.
- Data Management and Analytics: Track and trace solutions often include data management and analytics tools. This allows companies to analyze supply chain data, identify potential bottlenecks, optimize inventory levels, and make informed business decisions.
- Authentication and Anti-Counterfeiting Measures: The unique identifiers on the products allow consumers and stakeholders to verify the authenticity of a product using mobile apps, websites, or dedicated authentication platforms. This helps in detecting and preventing the circulation of counterfeit goods.
- Supply Chain Visibility and Transparency: Companies can track their products at each stage of the supply chain, providing complete visibility and transparency into the movement and location of goods.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, such as pharmaceuticals and tobacco, have stringent regulations that mandate the implementation of track and trace systems to ensure product safety and combat illegal trade.
- Consumer Engagement: Some track and trace solutions offer consumer engagement features, such as product information, promotions, and loyalty programs, accessed through scanning the product’s unique identifier.
Track and trace solutions are especially vital for industries dealing with high-value products, sensitive goods, and those that require adherence to strict regulatory standards. These solutions not only help in securing the supply chain but also build trust among consumers by assuring them of the product’s authenticity and origin.
Unique ID Generation
Unique ID generation refers to the process of creating identifiers that are guaranteed to be unique within a specific context or system. These IDs are typically used to distinguish and track individual entities, such as products, transactions, or users, within a database or across multiple systems.
Common methods for generating unique IDs include:
Sequential numbering: Assigning IDs in ascending or descending order, ensuring each new ID is one greater (or lesser) than the previous one.
UUID (Universally Unique Identifier): Generating IDs according to a standardized format that guarantees uniqueness across different systems and time periods.
Hashing: Using cryptographic hashing algorithms to generate unique IDs from input data, such as timestamps, user information, or random values.
Combination of factors: Combining multiple factors, such as timestamp, location, and random values, to create IDs that are highly likely to be unique.
The choice of method depends on factors such as the scale of the system, performance requirements, and the level of uniqueness needed.
Warehouse Management Solutions
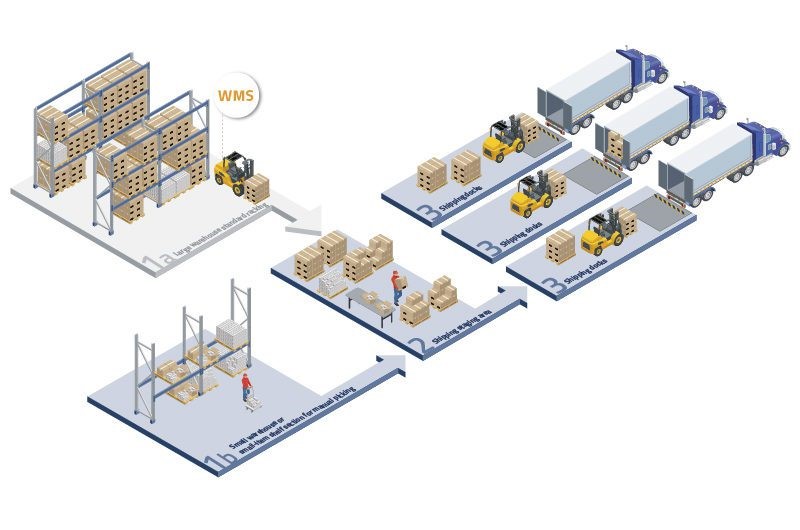
Warehouse management solutions are software systems and technologies designed to efficiently manage and optimize the operations of a warehouse or distribution center. These solutions provide a comprehensive set of tools and functionalities that help businesses streamline their inventory management, order processing, and overall warehouse operations. By using warehouse management solutions, companies can improve productivity, reduce costs, minimize errors, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Key features and components of warehouse management solutions include:
- Inventory Management: The system keeps track of all inventory levels, locations, and movements within the warehouse. It enables real-time visibility of stock levels, automates inventory replenishment, and helps prevent stockouts and overstocking.
- Order Management: Warehouse management solutions facilitate order processing, from order creation to order fulfillment. They optimize order picking, packing, and shipping processes to ensure accurate and timely order delivery.
- Barcode and RFID Integration: Barcode and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technologies are often integrated with warehouse management systems to enable efficient and accurate item tracking and picking.
- Warehouse Layout and Slotting: The system can help optimize the warehouse layout and slotting strategies to minimize travel time for workers and reduce the time taken for order fulfillment.
- Labor Management: Warehouse management solutions may include labor management features to monitor worker productivity, track labor costs, and optimize workforce scheduling.
- Shipping and Transportation Management: The system may integrate with shipping carriers to streamline shipping label generation, track shipments, and manage transportation logistics.
- Reporting and Analytics: Warehouse management solutions provide comprehensive reporting and analytics tools that allow managers to analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) and make data-driven decisions to improve warehouse efficiency.
- Integration with ERP and E-commerce Platforms: Integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and e-commerce platforms ensures seamless data flow between different business functions and enables efficient order processing.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) Integration: In some advanced warehouse setups, warehouse management systems can be integrated with AGVs for autonomous material handling.
Benefits of Warehouse Management Solutions:
- Improved Efficiency: By automating processes and optimizing workflows, warehouse management solutions enhance overall warehouse efficiency and reduce operational bottlenecks.
- Increased Accuracy: Automated data capture and order processing reduce the likelihood of human errors in inventory management and order fulfillment.
- Real-time Visibility: Warehouse managers have real-time visibility into inventory levels, order statuses, and other critical warehouse data, enabling proactive decision-making.
- Cost Savings: Streamlining warehouse operations leads to reduced labor costs, minimized inventory carrying costs, and improved space utilization.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Faster and accurate order fulfillment results in improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Warehouse management solutions are essential tools for modern supply chain management. They enable businesses to adapt to dynamic market demands, efficiently handle inventory, and deliver products to customers in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Conveyor Solutions
A conveyor solution refers to a system of conveyors designed to transport goods, materials, or products within a facility or between different locations. Conveyor systems are widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, distribution, and logistics, to automate material handling processes and improve efficiency.
Key components of a conveyor solution include:
- Conveyor belts: The primary component that carries goods along a predefined path within the facility. Conveyor belts come in various types, such as flat belts, roller belts, and modular belts, each suitable for different applications and load capacities.
- Conveyor rollers: Used to support and guide conveyor belts, rollers can be powered or gravity-driven and help facilitate smooth movement of goods along the conveyor system.
- Motorized drives: Electric motors and drives provide the necessary power to move conveyor belts and control the speed and direction of material flow.
- Control systems: Automation control systems manage the operation of the conveyor system, including start/stop functions, speed control, and integration with other equipment or processes.
- Sensors and detectors: These devices are used to detect the presence of items on the conveyor, monitor conveyor performance, and ensure safe operation by detecting jams or blockages.
- Sortation systems: Incorporating mechanisms such as diverters, switches, and sorters, sortation systems enable the separation and routing of items to different destinations based on predefined criteria, such as destination, size, or weight.
Conveyor solutions offer numerous benefits, including increased throughput, reduced labor costs, improved safety, and enhanced operational flexibility. They can be customized to meet specific application requirements and integrated with other material handling equipment to create comprehensive automation solutions for warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities.
Print and Apply Solutions
A print and apply solution is a system used for printing labels on-demand and applying them to products, packages, or containers as they move along a production line or through a warehouse. These solutions are commonly used in manufacturing, logistics, and distribution environments to automate the labeling process and ensure accurate and efficient product identification and tracking.
Key components of a print and apply solution include:
- Label printer: A printer capable of printing labels with variable data, such as product information, barcodes, serial numbers, and expiration dates, based on input from a computer or control system.
- Applicator mechanism: A device equipped with a labeling head or applicator that dispenses labels onto products or packaging with precision and consistency. The applicator can use various methods, such as blow-on, tamp-on, or wipe-on, depending on the application requirements and packaging characteristics.
- Control system: A software or control interface that coordinates the printing and application process, including label design, data input, printing commands, and synchronization with conveyor or production line speed.
- Sensors and scanners: Sensors and scanners are used to detect products or containers on the conveyor line, verify label placement and alignment, and ensure accurate labeling.
- Integration with other systems: Print and apply solutions can be integrated with other equipment, such as barcode scanners, weighing scales, and vision systems, as well as with enterprise systems like warehouse management systems (WMS) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, to streamline data exchange and process automation.
By implementing a print and apply solution, businesses can improve labeling accuracy, reduce labor costs, increase operational efficiency, and enhance traceability and compliance with labeling regulations. These solutions are scalable and customizable to meet the specific needs of different industries and applications.
 Connect with us
Connect with us
